A couple of vital features of an Online Transaction Processing system are atomicity and concurrency. Atomicity ensures that when one step fails or remains incomplete at the time of transaction then the entirety won’t continue. On the other hand, concurrency prevents several users from changing the same data simultaneously. For making a transaction complete successfully every database change should be permanent and this condition is called atomic statefulness.
For averting single points of failure, the systems of OLTP are habitually decentralized. Some classic instances of OLTP systems are considered retail sales, financial transaction systems, and order entry.
We allow students to pay our fees through various mediums and so, students do not face any difficulty in paying our fees. This is one of the several reasons for which students count on us for buying assignment help with Online Transaction Processing.
The Method of Using OLTP
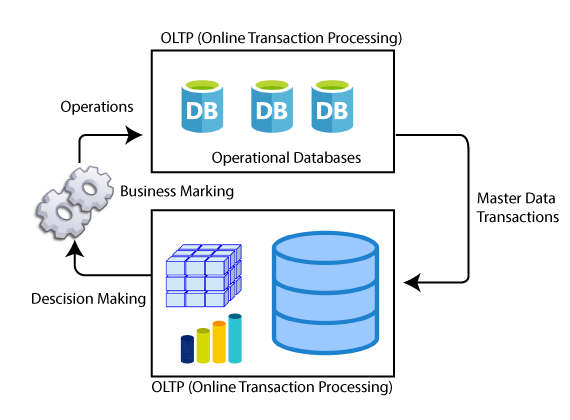
Commonly, OLTP includes updating, inserting, and also deleting little amounts of data and a typical instance of the technology of OLTP is an ATM. The databases that OLTP handles turn the source of data for OLAP or Online Analytical Processing, data retrieving, and online analysis process that got into the BI space more than two decades ago.
The Value that OLTP Proposes
As OLTP systems habitually serve a huge number of users and they habitually handle mission-critical data, they commonly need high obtainability as well as security protocols.
- Indexed entree to data
- Speedy time of responses
- Numerous users
- Transactions that involve little amounts of data
- Frequent queries and updates
Benefits of OLTP
OLTP is capable of dealing with numerous transaction requests concurrently and the backup capability reliably and continue when the portion of a system fails. It permits its users to do some operations, like writing, reading and deleting data fast.





 3 Bellbridge Dr, Hoppers Crossing, Melbourne VIC 3029
3 Bellbridge Dr, Hoppers Crossing, Melbourne VIC 3029
