Autonomy, variety, and authority of decision-making are the ways to add challenge to jobs. Job rotation and job enrichment are the ways to add challenge and variety.
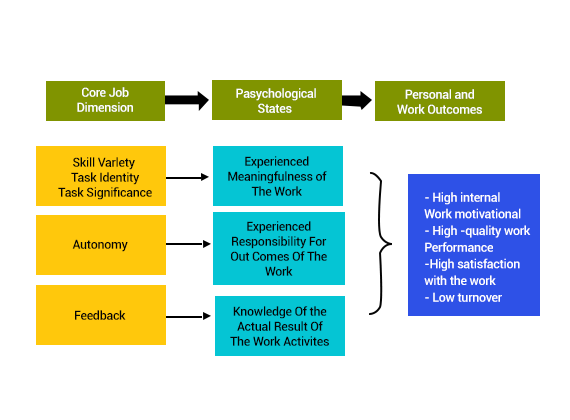
The theory states that if the five core job features including task identity, skill variety, autonomy, task importance, and feedback are added then they shall impact the three important psychological states such as knowledge of the real results, experienced meaningfulness, and experienced responsibility that in turn can influence the work outcomes (absenteeism, job satisfaction, and work motivation). These five job characteristics may be integrated and form a MPS or motivational potential score that can be used how a job might affect the behaviour and attitude of an employee.
The Application of Oldham and Hackman Job Design Theory in Workplaces
This model was properly received because the findings were precise and clear and be applied easily in the workplace. The five features can be used as checklists for job review or job creation. For instance, in a job designing stage, the employers can ask whether there are several tasks to break the monotony or whether a job was placed clearly to understand its relevance.
Two motivational methods have developed from this job theory such as job enrichment and job rotation. Job enrichment involved engaging elements. An example is asking experienced employees to undertake to coach, showing recognition, and adding interest. In job enrichment, it includes small working groups, employee-owned councils, and job rotation. You can know more in our Oldham and Hackman Job Design Theory assignment writing help.
In job rotation, employees are given tasks that are performed normally by colleagues and it breaks up the work. Many organizations use job rotation for filling up temporary positions that can improve employee satisfaction, widens organizational knowledge, and teaches new skills.




 3 Bellbridge Dr, Hoppers Crossing, Melbourne VIC 3029
3 Bellbridge Dr, Hoppers Crossing, Melbourne VIC 3029

