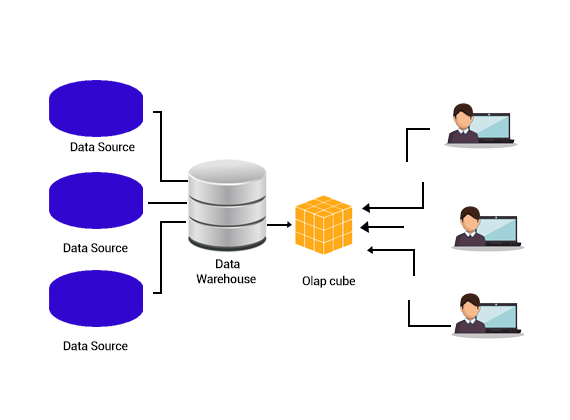
OLAP is a foundation for multiple business applications for Business Planning, Business Performance Management, Forecasting, Budgeting, Financial Analysis, Reporting, Knowledge Discovery, Simulation Models, and Data Warehousing Reporting. It allows end-users in performing data ad-hoc analysis in many dimensions thus offering insight and understanding their needs for good decision-making.
The OLAP databases have one or more than one cube. The cubes have been designed in a manner that reports creating and viewing become easy.
What are the Kinds of OLAP?
The different kinds of OLAP are discussed in our OLAP assignment help online as follows:
Relational OLAP or ROLAP: It works with data that is present in relational databases. The facts tables are stored as relational tables. It enables multidimensional data analysis and it is the fastest-growing OLAP.
Multidimensional OLAP: It uses an array-based storage engine used for displaying multidimensional data views. They use the OLAP cubes.
Hybrid OLAP: It is a combination of MOLAP and ROLAP> It provides quick computation and greater scalability of ROLAP. It uses the following two databases:
- Computed or aggregated data is stored in multidimensional OLAP cubes.
- The entire information is saved in a relational database.
Desktop OLAP or DOLAP: In this OLAP, users download a portion of data from a local warehouse or on the desktop for analyzing it. It is cheap for deployment because it provides a few functionalities compared to other OLAPs.
Web OLAP or WOLAP: Web OLAP is an OLAP system that is accessed through a web browser. It is a 3-tier architecture consisting of three parts such as client, middleware, and database servers.
Mobile OLAP: It enables users in accessing and analyzing OLAP data with mobile devices.
Spatial OLAP or SOLAP: It is creating for facilitating management of spatial as well as non-spatial data in a GIS or Geographic Information System.




 3 Bellbridge Dr, Hoppers Crossing, Melbourne VIC 3029
3 Bellbridge Dr, Hoppers Crossing, Melbourne VIC 3029

