MVC separates the presentation layer and business logic from one another. This was used traditionally for desktop GUIs or Graphical User Interfaces. These days, MVC has become popular to design web applications and mobile apps.
The model plays a vital role in MVC. It transfers data between controller and view. It can retrieve data from database and other web services, In MVC, the component is used for designing the web pages that are UI logic of the application. Our team of acadmeic tutors have extensive experience to write assignments on ASP.NET MVC framework.
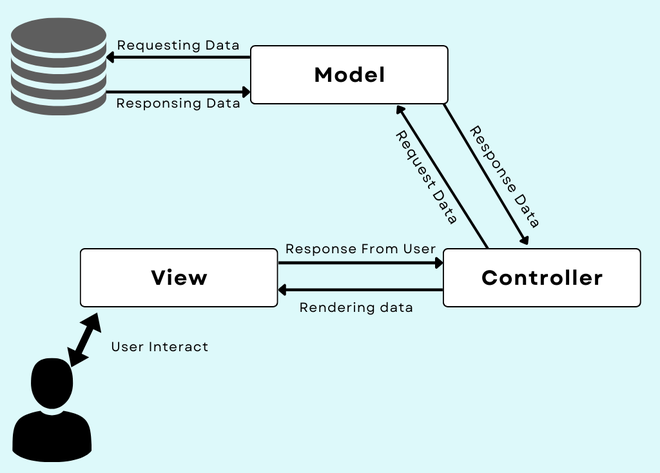
The Components of MVC
The components of MVC are discussed in our MVC Framework assignment help as follows:
Model: The Model stores data and related logic. It presents data, which is being transferred between the controller components and the related business logic. The controller shall retrieve the info of customers from the database. This manipulates data and then send it back to the database. It responds to requests from views and instructions from controllers. It is the lowest pattern level that is responsible to maintain data.
View: It is a part of an application that represents data presentation. Views are build from the data gathered from model data. It requests the model to provide information so that the output presentation is resent to users. It represents data from diagrams, charts, and table.
Controller: It is the part of an application, which handles user interaction. It interprets the keyboard and mouse inputs from users thus informing view and model for changes as appropriate. It sends commands to a model. The controller sends commands to the associated view for changing the view’s presentation.
Features of MVC
- Frictionless and easy testing. Highly extensible, testable, and pluggable framework.
- Offers complete control over URLs and HTML
- Clear separation of Model, View, and Controller. There is also the separation of application jobs such as UI logic, business logic, and input logic.
- Supports RDD or Test-Driven Development
- URL Routing for URLs.
- Leveraging the existing features offered by JSP, ASP.NET, Django, etc




 3 Bellbridge Dr, Hoppers Crossing, Melbourne VIC 3029
3 Bellbridge Dr, Hoppers Crossing, Melbourne VIC 3029

